
📘 Introduction to Analog Computer
An Analog Computer is a type of computer that works with continuous data. It processes information represented by physical quantities such as voltage, current, speed, pressure, temperature, or sound waves.
Unlike digital computers that use binary numbers (0 and 1), analog computers use continuous signals to perform calculations. They measure and solve mathematical problems using real-world physical values.
Analog computers were widely used before digital computers became popular.
🔤 Meaning of “Analog”
The word analog means “similar” or “comparable.” An analog computer represents data in a form that is similar to the physical quantity being measured.
For example:
- A thermometer measures temperature continuously.
- A speedometer shows vehicle speed in real time.
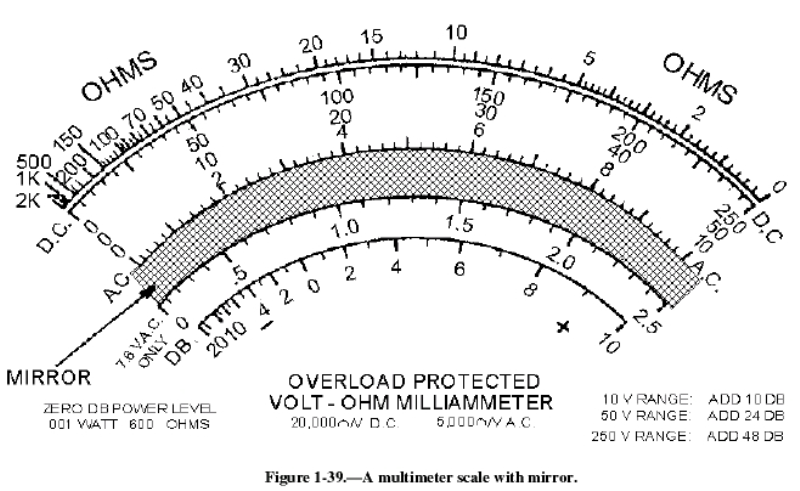
- A voltmeter measures electrical voltage.
These devices do not convert data into binary numbers. Instead, they directly display continuous values.
⚙️ Basic Components of an Analog Computer
Analog computers include the following parts:
1️⃣ Input Devices
These devices measure physical quantities.
Examples:
- Temperature sensors
- Pressure sensors
- Speed sensors
2️⃣ Processing Unit
Performs calculations using electrical or mechanical components.
3️⃣ Output Devices
Displays results in the form of meters or dials.
Examples:
- Analog meter
- Graph plotter
- Gauge
🔄 Working of Analog Computer
Analog computers work by:
- Measuring a physical quantity
- Converting it into electrical signals
- Performing calculations using circuits
- Displaying the output continuously
For example, in a flight simulator, speed and altitude are calculated using analog systems.
🏗️ Types of Analog Computers
🛠️ Mechanical Analog Computers
Use gears and wheels to perform calculations.
Example: Slide rule.
⚡ Electrical Analog Computers
Use electrical signals for calculations.
Example: Early scientific research machines.
🌟 Characteristics of Analog Computer
Analog computers have the following features:
- 📏 Works with continuous data
- ⚡ Fast calculation for specific tasks
- 📊 Provides real-time output
- 🎯 Less accurate than digital computers
- 🔄 Used for simulation and measurement
🏢 Applications of Analog Computers
Analog computers are used in:
🚗 Automobiles
- Speedometer
- Fuel gauge
🏥 Healthcare
- ECG machines
- Blood pressure monitors
✈️ Aviation
- Flight simulators
- Navigation systems
🌡️ Weather Forecasting
- Measuring temperature and pressure
🏭 Industries
- Process control systems
👍 Advantages of Analog Computer
- Real-time data processing
- Simple design for specific tasks
- Faster for continuous measurements
- No need for complex programming
👎 Disadvantages of Analog Computer
- Less accurate
- Difficult to store data
- Limited memory
- Hard to modify or reprogram
- Mostly replaced by digital computers
🔍 Difference Between Analog and Digital Computer
| Feature | Analog Computer | Digital Computer |
|---|---|---|
| Data Type | Continuous | Binary (0 & 1) |
| Accuracy | Moderate | High |
| Storage | Limited | Large |
| Example | Thermometer | Laptop |
🔮 Modern Use of Analog Technology
Although digital computers are widely used today, analog technology still exists in:
- Audio equipment
- Measurement devices
- Control systems
- Scientific instruments
Many modern systems combine analog and digital technology, called Hybrid Computers.
📌 Conclusion
An Analog Computer is a computing device that processes continuous data using physical quantities. It is mainly used for measurement, simulation, and control systems. Although digital computers have replaced most analog systems, analog computers are still important in specific applications where real-time continuous data processing is required.
If you want, I can also write