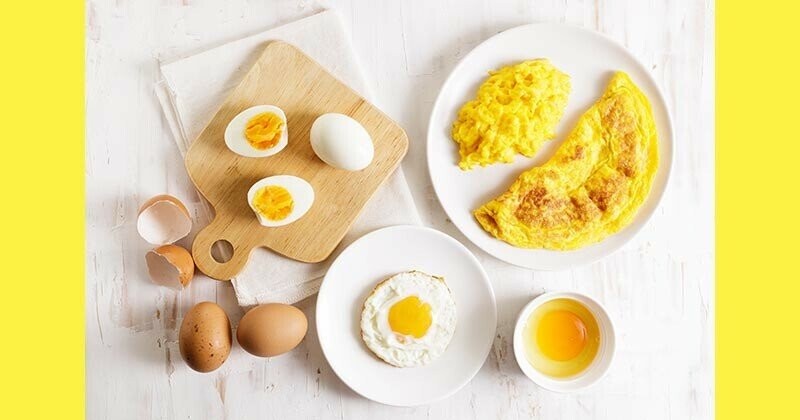
The healthiness of a boiled egg versus an omelette depends on several factors, including your dietary needs, preparation methods, and additional ingredients in the omelette.
Here’s a comparison to help you decide:
1. Basic Nutrition (Per Large Egg, ~50g)
| Preparation | Calories | Protein | Fat | Carbs |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Boiled Egg | 68 | 6g | 5g | 0g |
| Plain Omelette | 93 | 6g | 7g | 0g |
- Boiled Egg: Lower in calories and fat because no oil or butter is used.
- Omelette: Higher in calories due to added fats from cooking oils or butter.
2. Additional Ingredients in Omelettes
- Omelettes often include ingredients like vegetables, cheese, or meats, which can add nutritional value (fiber, vitamins, protein) or extra calories, fat, and sodium.
- Choose nutrient-rich additions like spinach, tomatoes, mushrooms, or bell peppers.
- Avoid high-calorie add-ons like processed meats and excessive cheese for a healthier option.
3. Cooking Method Matters
- Boiled Egg: Requires no added fat, making it ideal for low-fat diets.
- Omelette: Often cooked with oil or butter, which can add unhealthy fats if not controlled. Use non-stick pans or healthy oils (e.g., olive or avocado oil) to reduce unhealthy fats.
4. Satiety and Customization
- Boiled Eggs: Provide a quick, nutrient-dense snack or breakfast with minimal preparation.
- Omelettes: More customizable, allowing for the inclusion of additional nutrients (like fiber from veggies).
5. Dietary Considerations
- For Weight Loss: Boiled eggs are a better choice due to their lower calorie content.
- For Nutrient Variety: Omelettes can be healthier if packed with vegetables and cooked with minimal oil.
- For Heart Health: Prefer boiled eggs or use minimal healthy fats in omelettes.
Verdict
- Boiled Eggs: Best for simplicity, weight management, and minimal calorie intake.
- Omelettes: Best for variety and enhanced nutrient content when prepared healthily.