Cybersecurity in 2026: The Rise of AI-Driven Threats
Cybersecurity is evolving faster than ever. As businesses continue accelerating digital transformation, cybercriminals are leveraging advanced technologies—especially Artificial Intelligence—to launch smarter, faster, and more devastating attacks. In 2026, cybersecurity is no longer just an IT concern; it is a business survival strategy.
AI-Powered Cyber Attacks Are Increasing
One of the biggest trends today is the use of AI by hackers. Cybercriminals are using machine learning algorithms to automate phishing campaigns, generate realistic deepfake content, and bypass traditional security systems. AI-generated phishing emails now mimic writing styles, corporate communication formats, and even personal messaging patterns, making them harder to detect.
Attackers are also using AI to scan systems for vulnerabilities in real-time. Instead of manually probing networks, automated bots can identify weaknesses and exploit them within minutes. This drastically reduces response time for defenders and increases damage potential.
Ransomware 2.0: More Targeted and Destructive
Ransomware continues to dominate the threat landscape, but it has evolved. Modern ransomware attacks are highly targeted. Instead of randomly infecting users, attackers now study organizations before launching attacks. They identify high-value data, map internal systems, and strike during peak operational hours.
Double extortion tactics are now common. Hackers not only encrypt data but also threaten to publish sensitive information if ransom is not paid. Industries such as healthcare, finance, and manufacturing are prime targets because downtime directly impacts revenue and lives.
Organizations must move beyond basic antivirus software and adopt advanced endpoint detection and response (EDR) systems.
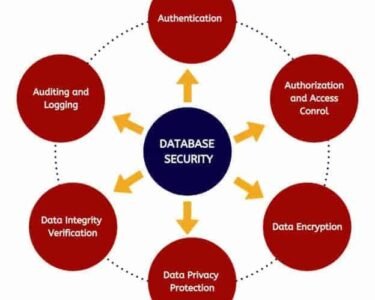
Zero Trust Security Is Becoming the Standard
The traditional “trust but verify” approach is outdated. Today’s model is “never trust, always verify.” Zero Trust Architecture (ZTA) ensures that no user or device is trusted automatically—even if they are inside the corporate network.
Zero Trust works on three key principles:
- Continuous identity verification
- Least-privilege access control
- Micro-segmentation of networks
By limiting access rights and constantly validating credentials, organizations reduce the risk of lateral movement within networks. Even if attackers gain access, they cannot easily spread.
Cloud Security Challenges Continue to Grow
With remote work and cloud adoption increasing, misconfigured cloud environments have become a major vulnerability. Many breaches occur due to improperly configured storage buckets, exposed APIs, or weak identity access controls.
Businesses must implement:
- Strong Identity and Access Management (IAM) policies
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
- Continuous cloud security monitoring
- Regular security audits
Cloud providers offer strong security tools, but responsibility is shared. Companies must actively configure and manage their security settings.
The Human Factor Remains the Weakest Link
Despite technological advancements, human error continues to cause security incidents. Weak passwords, clicking malicious links, and ignoring update prompts expose systems to attackers.
Regular cybersecurity awareness training is critical. Employees must learn how to identify phishing attempts, suspicious downloads, and unusual system behavior. Security is no longer the IT department’s job alone—it is everyone’s responsibility.
Proactive Security Is the Future
Reactive security strategies are no longer sufficient. Organizations must adopt proactive threat hunting, real-time monitoring, and automated incident response systems.
Key proactive strategies include:
- Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) systems
- AI-driven anomaly detection
- Regular penetration testing
- Backup and disaster recovery planning
Cyber resilience is the ultimate goal. Even if attacks occur, businesses must ensure minimal downtime and quick recovery.
Final Thoughts
Cybersecurity in 2026 demands a strategic approach. AI-powered threats, advanced ransomware tactics, and expanding cloud infrastructures require organizations to rethink their defense strategies.
The key takeaway is clear: cybersecurity is not optional—it is foundational. Companies that invest in Zero Trust frameworks, AI-driven defense tools, employee awareness, and proactive monitoring will stay ahead of attackers.
The cyber battlefield is evolving. The question is not whether attacks will happen—but whether your organization is prepared.