Android Smartphone Exports from India Grow Rapidly in 2025 Due to US Tariffs and Indian Incentives
The momentum of Android smartphone exports from India is gaining unprecedented pace, driven by shifting global trade policies and India’s enhanced manufacturing ecosystem. As the US imposes heavy tariffs on Chinese and Vietnamese imports, India is quickly emerging as a favorable export base for both Android and Apple smartphone manufacturers.
In 2025, a combination of US tariff regulations and India’s export promotion schemes has catalyzed a major transition in smartphone supply chains. Leading Android brands like Motorola and Samsung have significantly ramped up production and shipments from India to North America, mirroring Apple’s successful export model.
Motorola Leads Android Smartphone Exports from India to the US
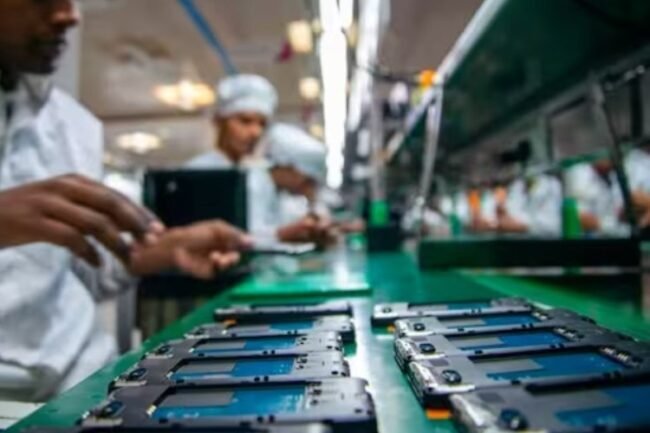
According to the latest data from market research firm Canalys, cited in a report by the Economic Times, Motorola, under Lenovo’s ownership, has exported 1.6 million Android smartphones from India in the first five months of 2025 alone. Notably, 99% of these exports were shipped to the United States, reflecting a sharp rise from 1 million units in 2024.
Motorola’s Indian production is handled through a key partnership with Dixon Technologies, an established electronics manufacturing services provider. Until recently, Motorola primarily relied on Chinese manufacturing hubs to supply the US market. However, with China now subject to a 55% US import tariff as of April 2025, India—with a lower tariff of 26%—has become a more viable alternative.
While smartphones are temporarily exempt from certain tariffs, the uncertain policy outlook in Washington has prompted manufacturers to seek long-term diversification and reduce over-reliance on Chinese facilities.
Samsung Joins the Export Surge from India
Samsung, another major player in the Android smartphone segment, is also significantly expanding its export base in India. Between January and May 2025, Samsung shipped 945,000 units of Android smartphones from India to the US—up from 645,000 units over the same period in 2024, according to Canalys.
Samsung’s traditional export base, Vietnam, is currently subject to a 46% tariff on US-bound smartphone exports. While these tariffs are temporarily suspended for 90 days amid ongoing trade negotiations, Samsung is clearly hedging its bets by scaling up Indian operations to ensure supply chain continuity.
Apple Still Dominates Smartphone Exports from India
While Android smartphone brands are accelerating their export strategies, Apple remains the dominant exporter in India’s smartphone manufacturing ecosystem. Apple has invested heavily in Indian manufacturing over the past few years and continues to lead the charge in terms of volume and value of smartphones exported to the US.
This diversification aligns with Apple’s broader strategy to reduce dependency on Chinese manufacturing amidst growing geopolitical tensions.
Dixon Technologies Expands Production Capacity
In response to the surging demand, Dixon Technologies—the key Indian manufacturing partner for Motorola—has announced a 50% increase in production capacity, specifically tailored to meet rising export volumes to North America.
During a recent earnings call, Dixon’s Managing Director, Atul Lall, confirmed that this expansion is primarily aimed at fulfilling US-bound orders, driven by ongoing tariff impacts and strategic manufacturing shifts.
India’s Role in the Future of Global Smartphone Supply Chains
The rise in Android smartphone exports from India reflects a broader realignment in global electronics manufacturing. As the US seeks to reduce trade dependency on China and Vietnam faces growing tariff risks, India is capitalizing on the opportunity by strengthening its position as a global production and export hub.
With initiatives like PLI (Production Linked Incentives) and increased partnerships between global OEMs and Indian manufacturers, the future looks promising for smartphone production in India. The export trend is expected to grow even further as brands continue to navigate the complexities of international trade dynamics.